No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.

With the ever-expanding digital landscape, cyberbullying has become a harsh reality for many. Michigan, recognizing its seriousness, has established specific laws to address this issue.
MCL 750.411x defines cyberbullying as posting a message in a public online forum about someone with the intent to threaten them with violence. This means simply posting something mean online doesn’t qualify as cyberbullying under this law.
However, if the post expresses a clear intention to harm the person, putting them in fear of bodily injury or death, it might be considered cyberbullying.
Definition
(6) As used in this section:
A first offense is punishable as a misdemeanor with up to 93 days in jail and a $500 fine. If the offender has a prior cyberbullying conviction, the penalties increase to a maximum of 1 year in jail and a $1,000 fine. Remember, these are just the legal consequences; cyberbullying can also have lasting social and emotional repercussions.
Have your rights been violated?
Have your driving priviledges been revoked?
Has your professional license been suspended?
Second Amendment rights taken away?
Have you been charged with a crime?
Call our office to see if we can help
Komorn Law 248-357-2550
If you encounter cyberbullying, don’t engage. Report the incident to the platform where it occurred and keep evidence like screenshots. Consider talking to a trusted adult or seeking help from organizations like Cyberbullying Research Center or StopBullying.gov. Remember, you’re not alone.
MCL 750.411x serves as a safeguard against online threats, but remember, online safety is a shared responsibility. By understanding the law, respecting others, and reporting harmful behavior, we can create a more positive and inclusive digital space for everyone.

Related Articles
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.

The steps to restore your driver’s license in Michigan vary depending on the reason your license was revoked or suspended. However, there are some general steps that apply to all cases:
The cost to restore your driver’s license in Michigan varies depending on the reason your license was revoked or suspended. It may be harder to get it back if you have numerous or other charges linked to the supension. You will most likely need an Attorney to fight for you.
There is a standard reinstatement fee of $125. You may also have to pay additional fees, such as the cost of any required driver improvement courses.
Have your rights been violated?
Have your driving priviledges been revoked?
Has your professional license been suspended?
Second Amendment rights taken away?
Have you been charged with a crime?
Call our office to see if we can help
Komorn Law 248-357-2550
It is not required to have a lawyer to restore your driver’s license in Michigan. However, a lawyer can help you understand the process and prepare for your hearing. If you have a complex case, or if you are not sure how to proceed, it is a good idea to consult with an attorney.
The amount of time it takes to restore your driver’s license in Michigan varies depending on the reason your license was revoked or suspended. If you have all of the required documentation and you are able to present a strong case to the SOS hearing officer, your license may be reinstated relatively quickly.
However, if your case is complex or if you have a history of driving offenses, it may take longer to get your license back.
You can find more information about restoring your driver’s license in Michigan on the Michigan Secretary of State website:
You can also contact the SOS Driver’s License Restoration Division at 517-322-1946 for more information.

Related Articles
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.

Involuntary manslaughter differs from murder in that it lacks intent to kill.
In Michigan, it is somewhat defined as the killing of another person through:
Involuntary manslaughter distinguishes itself from voluntary manslaughter based on the intent of the alleged offender.
The broad differentiating factor lies in whether the accused intended to cause severe physical harm to the victim, as seen in cases of voluntary manslaughter.
Conversely, in cases of involuntary manslaughter, the accused is alleged to have caused the victim’s death without malice or intent.
A conviction of voluntary manslaughter can arise when the accused did not have the intention to cause serious bodily harm to the victim but exhibited a significant lack of care in their behavior towards the victim’s safety.
The determining factor between these two homicide offenses is typically the presence of intent.
Charged with Homicide, Second Degree Murder, Manslaughter?
Call our office to see if we can help
Komorn Law 248-357-2550
Beyond the legal penalties, a conviction for involuntary manslaughter can have lasting consequences, including:

Related Articles
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.

Treasury: Adult-Use Marijuana Payments Being Distributed to Michigan Municipalities and Counties; More Than $59.5 Million Going to 224 Municipalities and Counties.
Sales of “legal” marijuana in Michigan contributed $266.2 million in tax revenue to the government during the most recent fiscal year, according to a new report from the legislature’s nonpartisan House Fiscal Agency.
That’s more than the state made from the sale of beer, wine and liquor combined.
February 28, 2023
The Michigan Department of Treasury today announced that more than $59.5 million is being distributed among 224 municipalities and counties as a part of the Michigan Regulation and Taxation of Marijuana Act.
Over the next few days, 81 cities, 26 villages, 53 townships and 64 counties will receive payments from the Marihuana Regulation Fund. For the state of Michigan’s 2022 fiscal year, this means each eligible municipality and county will receive more than $51,800 for every licensed retail store and microbusiness located within its jurisdiction.
“Municipalities and counties will begin seeing these payments appear in their banking accounts,” State Treasurer Rachael Eubanks said. “Through a partnership, the dollars received from the adult-use marijuana taxes and fees are distributed to our participating communities.”
Revenue was collected from 574 licensees among the state’s cities, villages and townships during the 2022 fiscal year. Some of these municipalities host more than one licensed retail store and microbusiness.
For the 2022 state fiscal year, there was $198.4 million available for distribution from the Marihuana Regulation Fund.
State law outlines how much is distributed from the Marihuana Regulation Fund.
Aside from the more than $59.5 million in disbursements to municipalities and counties, $69.4 million was sent to the School Aid Fund for K-12 education and another $69.4 million to the Michigan Transportation Fund.
In total, more than $1.8 billion in adult-use marijuana sales was reported for Fiscal Year 2022.
“The team at the CRA does an amazing job and our effective regulatory approach allows our licensees to provide Michigan’s cannabis consumers the safest possible product,” said CRA Executive Director Brian Hanna. “The funding that makes its way to local governments through the excise tax collected by licensed retailers is an important benefit of the regulated cannabis industry and the CRA is committed to doing our part in supporting our law-abiding licensees.”
Adult Use Break Downs
$226m – $59m = $167m (left over after distribution…nice haul)
Marijuana funds collected under the Michigan Regulation and Taxation of Marihuana Act (Initiated Law 1 of 2018) are distributed, upon appropriation, as follows:
Links
For more information about adult-use marijuana tax distributions – including a breakdown of how much municipalities and counties received – go to Michigan.gov/RevenueSharing. To learn more about Michigan’s adult-use marijuana industry, go to Michigan.gov/cra.
Source: https://www.michigan.gov/treasury/news/2023/02/28/adult-use-marijuana-payments-being–distributed-to-michigan-municipalities-and-counties
Have your rights been violated?
Have your driving priviledges been revoked?
Has your professional license been suspended?
Second Amendment rights taken away?
Have you been charged with a crime?
Call our office to see if we can help
Komorn Law 248-357-2550
Legislative Update 12-9-22
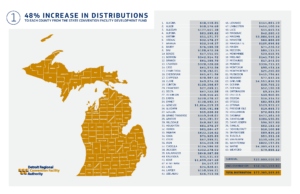 A two-bill package designed to extend the capture of liquor tax revenue that counties use for substance abuse programs passed during the last days of the legislative session this week and will soon mean a $25 million boost to counties.
A two-bill package designed to extend the capture of liquor tax revenue that counties use for substance abuse programs passed during the last days of the legislative session this week and will soon mean a $25 million boost to counties.
Senate Bills 1222-23, by Sen Wayne Schmidt (R-Grand Traverse), amend the State Convention Facilities Authority Act to extend the sunset on the capture of liquor tax revenue for improvements to the convention facility in Detroit and therefore extend the sunset on the collection of liquor tax revenue for counties.
The issues were tied together when the act was created. Under current law, the collection and allocation of the liquor tax revenue expires once the bonds for the convention facility are paid off. Due to recent increases in liquor tax revenue, those bonds are scheduled to be paid off 13 years early, which would eliminate the future collection of revenue and deplete the allocation to counties. This two-bill package does not extend the 2039 deadline for the bonds to be paid off, but it does allow the facility authority to issue additional bonds for improvements.
MAC has been working with representatives from the authority to address our need to have counties’ annual allocation reflective of the collection of the liquor tax revenue. Current law states counties receive an increase in their allocation based on a percentage above the previous year’s allocation, not on a percentage of the total tax collected. The excess tax collected is instead allocated to the reduction of the bond debt of the authority. (Again, due to the increase in liquor tax revenue, those bonds are scheduled to be paid off early.)
By allowing the authority to issue additional debt for improvements, the bills do something significant for counties. Beginning in 2023, the baseline allocation in liquor tax dollars for counties will increase by approximately 48 percent — or $25 million. (See county-by-county estimates.) The annual increase will remain the same as current law of 1 percent additional each year, but the baseline will be reset every three years to reflect the increase in revenue from the liquor tax.
Also, current law states 50 percent of the liquor tax revenue received by counties must be allocated to substance abuse programs. SBs 1222-23 will change that requirement to 40 percent (though no less than the amount allocated in FY22). In short, this will be a significant increase in funds toward substance abuse programs and an increase in the amount counties can allocate to their general funds.
The bills are now headed to the governor for her expected signature.
For more information on this issue, contact Deena Bosworth at bosworth@micounties.org.

Related Articles
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.

Domestic Violence
The legislature passed a package of bills that add subsets to certain misdemeanor offenses (identified below) for offenses involving domestic relationships.
See 2023 PA 199 (eff. Feb 13, 2024).
Violation of these provisions are considered domestic violence. Misdemeanors involving domestic violence are defined in MCL 750.224f(10)(c), amended by 2023 PA 201 (eff. Feb 13, 2024), and include the following:
Importantly, under MCL 750.224f(5), amended by 2023 PA 201 (eff. Feb 13, 2024), an offender convicted of a misdemeanor involving domestic violence, as listed above,
shall not possess, use, transport, sell, purchase, carry, ship, receive, or distribute a firearm or ammunition in this state until the expiration of 8 years after all of the following circumstances exist:
(a) The person has paid all fines imposed for the violation.
(b) The person has served all terms of imprisonment imposed for the violation.
(c) The person has successfully completed all conditions of probation imposed for the violation.
Have your rights been violated?
Have your driving priviledges been revoked?
Has your professional license been suspended?
Second Amendment rights taken away?
Have you been charged with a crime?
Call our office to see if we can help
Komorn Law 248-357-2550
In addition to domestic violence measures, 2023 PA 201 (eff. Feb 13, 2024) expands the definition of felony to include violations “punishable by imprisonment for a term exceeding 1 year.” MCL 750.224f(10)(b), amended by 2023 PA 201 (eff. Feb 13, 2024) (emphasis added). Previously, a felony was defined as a violation of law punishable by imprisonment for four or more years. Consequently, 2023 PA 201 increases the number of offenses that fall under the three-year firearms and ammunition prohibition in MCL 750.224f(1).
Juvenile Reforms
Screening Tools and Risk Assessment
2023 PA 287 (eff. Oct 1, 2024) amends the Juvenile Diversion Act, MCL 722.822, .823, .826, and .829, to allow the use of risk and mental health screening tools before a diversion decision for the minor is made. The amended act states that these tools may not be conducted on a minor who is either (1) accused or charged with a specified juvenile violation or (2) currently under supervision in the juvenile justice system by the court or the Department of Health and Human Services. A minor may not be diverted under the act unless a law enforcement official or court intake worker (1) receives the results of a risk screening tool and a mental health screening tool for the minor and (2) uses the results of the risk screening tool and the mental health screening tool as well as the best interests of public safety and the minor to inform the decision to divert the minor.
In addition, 2023 PA 289 (eff. Oct 1, 2024) amends MCL 712A.2f to require a court to consider the results of a screening before placing a juvenile’s case on the consent calendar. The results of a screen under these amendments are confidential case records.
The procedure for juvenile detention has also been modified. 2023 PA 290 (eff. Oct 1, 2024) amends MCL 712A.15 and .16 to state that before a juvenile may be detained in a secure facility pending hearing, an individual or agency must use a detention screening tool on the juvenile. The court then must consult those results and follow any rules regarding their use. The amendments further specify that any statement or incriminating evidence obtained during screening is not admissible as evidence in a court proceeding.
2023 PA 298 (eff. Oct 1, 2024) amends MCL 712A.18 to require a designated, trained individual or agency to conduct a risk and needs assessment for each juvenile before a disposition. The amendment also requires a court to consider the results of the assessment, in addition to other factors, when making a disposition decision. Finally, the amended statute requires an additional assessment if six months have passed, if the juvenile experienced a major life event, or if there was a major change in the juvenile’s proceedings.
Factors to Consider to Try a Juvenile as an Adult
Effective October 1, 2024, 2023 PA 291 amends MCL 712A.2d, .2f, and .4 by modifying the factors a court must consider before trying a juvenile as an adult. These factors now include
See MCL 712A.2d(2)(a)–(i), amended by 2023 PA 291 (eff. Oct 1, 2024).
Time to Complete Diversion
2023 PA 288 (eff. Oct 1, 2024) amends MCL 722.825 and .826 to limit the time a minor has to complete a diversion agreement to not exceed three months unless it is determined that a longer term is necessary.
Delinquent Accounts
2023 PA 292 (eff. Oct 1, 2024) amends MCL 600.4803 to exempt a juvenile or their parent or guardian from a late penalty if the juvenile failed to pay a fee or cost associated with the proceedings in 56 days. Furthermore, 2023 PA 293 (eff. Oct 1, 2024) amends MCL 769.1 to delete certain provisions relating to reimbursement for court fees in a juvenile case.
Crime Victims’ Rights
MCL 760.21b(1), added by 2023 PA 180 (eff. Feb 13, 2024), states in part that “[a] police officer or a prosecuting attorney may provide a domestic or sexual violence service provider agency with the name, demographics, and other pertinent information of, and information to facilitate contact with, a victim of domestic or sexual violence for the purpose of offering supportive services to the victim.”
2023 PA 179 (eff. Feb 13, 2024) amends MCL 780.758, .788, and .818 to specify that certain items already exempted under the Freedom of Information Act, such as pictures, photographs, drawings, or other visual representations, including any film, videotape, or digitally stored image of a victim that is made available through a public court proceeding streamed on the Internet or other means, may be blurred.
2023 PA 178 (eff. Feb 13, 2024) amends MCL 780.765, .793, and .825 to allow a victim to remotely provide an oral impact statement at a disposition or sentencing.
Reproductive Rights
Numerous bills were passed, including 2023 PA 205, 208, and 286 (all effective February 13, 2024), that codify the rights to reproductive freedom and repeal and modify certain acts to reflect this codification. The repealed or modified acts include the following:
Hate Crimes
2023 PA 277 (eff. Feb 13, 2024) added MCL 750.147c to the Michigan Penal Code to state that a person is guilty of institutional desecration if the offender “maliciously and intentionally destroys, damages, defaces, or vandalizes, or makes a true threat to destroy, damage, deface, or vandalize” specified institutions identified in MCL 750.147c(1)(a)–(g) “because of the actual or perceived race, color, religion, sex, sexual orientation, gender identity or expression, physical or mental disability, age, ethnicity, or national origin of another individual or group of individuals, regardless of the existence of any additional motivating factors.” The act includes felony and misdemeanor punishments, depending on the dollar value of the property damage or injury.
Vulnerable Adults
MCL 750.145h(1), added by 2023 PA 275 (eff. Mar 7, 2024), states in part that “[a] person shall not intentionally or knowingly harass, abuse, threaten, force, coerce, compel, or exploit the vulnerability of a vulnerable adult in a manner that causes the vulnerable adult to provide that person, or any other person, sexually explicit visual material.” The statute also provides for misdemeanor and felony penalties for these offenses.
Health Professionals
Numerous bills were passed to protect health professionals and medical volunteers. MCL 750.81, .81a, and .82, which govern assaults, were amended by 2023 PA 271 and 272 (both effective March 5, 2024) to specify that if the victim of an assault is a health professional or medical volunteer and the offense occurs while the victim is performing their duties, the offender is subject to an enhanced penalty. In addition, the statutes require health facilities to post prominent, visible signs about the enhanced penalty.
Elections
MCL 168.931b(1), added by 2023 PA 253 (eff. Feb 13, 2024), states in part that “[a]n individual who intimidates an election official because of the election official’s status as an election official, with the specific intent of interfering with the performance of that election official’s election-related duties, is guilty of a crime.” The new law also criminalizes actions that prevent an election official from performing their duties. It does not apply to “constitutionally protected activity,” such as “reporting, news gathering, protesting, lobbying, advocacy,” or other activities of public interest or concern.

Related Articles
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.