Driving under the influence of cannabis is illegal and carries serious consequences in Michigan.We have fought and won many cases from the District Courts, Circuit Courts, Court of Appeals and the Supreme Court through out the State of Michigan. We have also fought...

SEARCH & SEIZURE: Government Use of Drones
Drone Surveillance and the Fourth Amendment: A New Case
In a recent decision, the Michigan Court of Appeals held that persons have a reasonable expectation of privacy in their property against drone surveillance conducted without a warrant or pursuant to a recognized exception to the warrant requirement. The case, Long Lake Township v Maxon, involved a civil zoning dispute in which the Township used a drone to take aerial images of the Maxon property without consent or any other specific legal authorization.
The Court of Appeals found that drone surveillance of private property is necessarily more intrusive and “qualitatively different” than the use of airplanes and helicopters permitted under California v Ciraolo and Florida v Riley. The Court noted that drones can fly at lower altitudes and hover in place, allowing them to collect more detailed images and information about private property.
The Court also found that the use of low-altitude unmanned drones to conduct targeted surveillance of private property is more like the use of thermal imaging devices found to be a “search” in Kyllo v United States. In Kyllo, the Supreme Court held that the government’s use of a thermal imaging device to monitor the radiation of heat from a home was a Fourth Amendment search. The Court reasoned that the government’s use of the thermal imaging device was a physical intrusion into the home’s curtilage, which is an area around the home that is considered to be part of the home itself.
The Court of Appeals in Long Lake Township v Maxon found that the Township’s use of a drone to take aerial images of the Maxon property without consent was a similar physical intrusion into the Maxon property. The Court also noted that the existing law in Michigan recognizes a reasonable expectation of privacy and other legal protections against drone misuse.
The decision in Long Lake Township v Maxon is significant because it is one of the first cases to address the Fourth Amendment implications of drone surveillance. The Court’s decision provides clear guidance to law enforcement and other government agencies that they cannot use drones to conduct surveillance of private property without a warrant or a recognized exception to the warrant requirement.
Implications for Law Enforcement
The decision in Long Lake Township v Maxon has important implications for law enforcement agencies that use drones for surveillance purposes. Law enforcement agencies should review their policies and procedures to ensure that they are consistent with the Fourth Amendment requirements set forth by the Court of Appeals.
In general, law enforcement agencies should obtain a warrant before using a drone to conduct surveillance of private property. However, there are a few limited exceptions to the warrant requirement, such as when the surveillance is conducted in response to an emergency or when it is conducted in a public area where there is a diminished expectation of privacy.
Law enforcement agencies should also be aware that the Fourth Amendment may apply to the use of drones even if the surveillance is not conducted directly by the agency itself. For example, if a law enforcement agency contracts with a private company to conduct drone surveillance on its behalf, the agency may still be required to comply with the Fourth Amendment.
Have you been charged with driving while high?
Want to fight that charge!
Call Our Office for a Free Case Evaluation
The decision in Long Lake Township v Maxon is a significant development in the law of drone surveillance. The Court’s decision provides clear guidance that the Fourth Amendment protects people from warrantless drone surveillance of their private property. Law enforcement agencies and other government agencies should review their policies and procedures to ensure that they are consistent with the Court’s decision.
The Court found the use of low-altitude unmanned
drones to conduct targeted surveillance of private property
to be more like the use of thermal imaging devices found
to be a “search” in Kyllo v United States when used to
monitor the radiation of heat from a home, and further
noted the existing recognition of a reasonable expectation
of privacy and other legal protections against drone misuse
as found in MCL 259.322(3) and MCL 259.320(1) (See Below)
Act 436 of 2016
259.322 Operation of unmanned aircraft system; harassment, violation of order, or invasion of privacy prohibited; definition; individual registered as sex offender.
Sec. 22.
Act 436 of 2016
259.320 Criminal liability; offense committed with aid of an unmanned aircraft system; exception.
Sec. 20.
Did You Know
Michigan State Police Legal Updates
MSP Legal Update No. 153 (01/2023)
- Search & Seizure: The smell of marihuana, standing alone, no longer constitutes probable cause to search for that substance
- Vehicle Code: Violation for impeding traffic requires evidence the accused’s conduct actually affected the normal flow of traffic.
Legal Update No. 153 (01/2023)
MSP Legal Update No. 150 (01/2022)
- Vehicle Code: Persons under the age of 21 may be prosecuted for operating a motor vehicle with the presence of marihuana in their system
- Criminal Law: Ethnic intimidation based on gender includes harassing or intimidating another person because of the actual or perceived gender of that person.
Legal Update No. 150 (01/2022)
Legal Update No. 148 (09/2021)
Legal Update No. 148 (09/2021)
Legal Update No. 147 (03/2021)
More Posts

Legal Tip – Driving High on Cannabis in Michigan
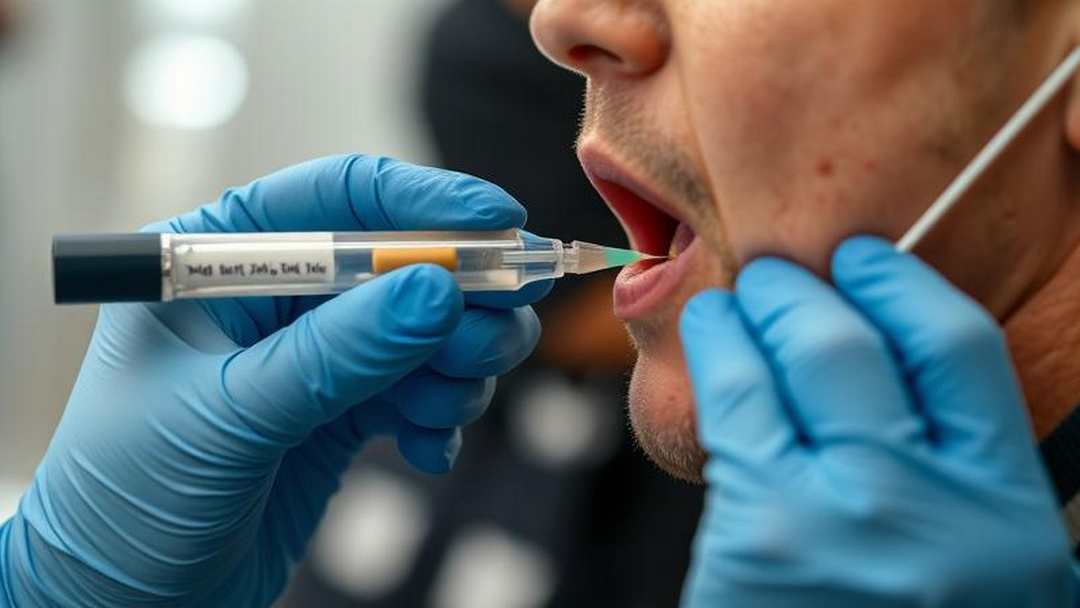
Michigan House Bill NO. 4391
It may just be easier to collect and analyze tears.This legislation seeks to integrate saliva testing for cannabis within law enforcement procedures, designating a refusal to participate in this testing as a criminal offense, similar to the penalties imposed for...

Legal Tip – Your Rights During a DUI Stop in Michigan
Komorn Law - Quick Legal TipsLegal Tip: Understanding Your Rights During a DUI Stop in Michigan A DUI stop can be stressful, but knowing your rights is crucial. You have the right to remain silent. You are not obligated to answer questions beyond basic identification....

How Much Does It Cost To Hire a Criminal Defense Attorney?
Don't do the crime - if you can't pay the price.Average Flat Fees. Some criminal defense attorneys charge a flat fee for certain types of cases, instead of billing by the hour. This may or may not include filing fees, motions, fees, etc. Flat fees include: DUI/DWI –...

What do you do when you are pulled over for suspected DUI?
If you are pulled over for suspected drunk driving you are probably going to be arrested. The less you say - the better off you are in the long run. If you find yourself being pulled over for suspected DUI, ensure you pull over safely to the roadside, maintain a...

One of Michigan’s Top DUI Attorneys
We aggressively defend all aspects of traffic law, from simple civil infractions to more serious alcohol and drug-related offenses. Don't wait till the last second to get an attorney. That's how you lose.Why Attorney Michael Komorn is one of Michigan’s Top DUI...

Michigan DUI Laws and Consequences – Second Offense
Michigan DUI Laws and Consequences – Second Offense Operating Under the Influence (OUI) is a serious offense in Michigan. If someone is caught driving under the influence of alcohol or drugs, they can face severe penalties. When it comes to a second offense, the...

Federal Ban on Owning Firearms by Cannabis Consumers is Unconstitutional Court Says
Federal charges against a non-violent, cannabis-using gun owner were unconstitutional.A federal appeals court panel upheld a lower court's ruling on Wednesday, declaring that federal charges against a non-violent, cannabis-using gun owner were unconstitutional. “The...

Michigan DUI Laws and Consequences – First Offense
First Offense DUI in Michigan: Laws and ConsequencesFacing a first offense DUI in Michigan can be daunting as the implications are significant and the legal landscape is complex. Understanding the laws surrounding Operating While Intoxicated is essential, as these...

Michigan Appeals Court Decision on Cannabis Use and Probation
Michigan Court of Appeals - Recreational Cannabis Use and ProbationRecently, another pivotal case, People v. Lopez-Hernandez, was decided by the Michigan Court of AppealsAt Komorn Law, we are dedicated to protecting the rights of our clients and staying at the...
